It is projected that the Log Management market will expand from USD 2.3 billion in 2021 to USD 4.1 billion by 2026 worldwide, demonstrating a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 11.9% during the period from 2021 to 2026.

Did you know that 2.5 quintillion bytes of data were generated worldwide every day, In 2018? And By 2025, the global data sphere will contain 175 zettabytes of data!
Enterprises are generating a colossal amount of data on a daily basis. The data is produced from multiple different sources and on a continuous basis.
Amidst the whole data explosion, Log data is overflowing as well. Log data comes from a range of sources such as applications, networks, systems, and users. As a result, they need an organized approach to manage and track diverse data across log files.
Log management is the process of collecting, monitoring, and analyzing logs and machine-generated data to gain insights into an organization’s operations. It helps to identify potential issues, debug errors, investigate security incidents, and provide compliance reports.
In other words, Log management is the process of collecting, storing, analyzing, and interpreting system and application logs to gain insights into the behavior of systems and applications.
Here are some key points to help you understand what log management is about:
- A variety of sources generate logs, including operating systems, applications, and network devices.
- One can store logs in different formats, such as plain text, CSV, or JSON, depending on the source and the log management tool used.
- It can involve both real-time monitoring and historical analysis of logs.
- It can help identify system performance, security, and compliance issues.
- Effective log management requires the use of specialized tools and technologies that can automate log collection, storage, and analysis.
- Log management can be an essential component of an organization’s security and compliance strategy, as logs can provide evidence of activity used in investigations or audits.
- Some common tools include log aggregators, log analysis platforms, and security information and event management (SIEM) systems.
Log Management Categories
Typically, log management is categorized into several key areas. Each category plays an essential role in managing and analyzing log data for various purposes such as troubleshooting issues, detecting anomalies, identifying security threats, and monitoring system performance.
Let’s go through them:
Collection: This involves using a tool to gather information from various sources, such as the operating system, servers, applications, endpoints, and users within an organization.
Monitoring: Log monitoring tools are used to keep track of events and activities and when they occurred.
Analysis: Log analysis tools are used to review the log collection from the log server and proactively identify issues such as bugs, security threats, or other problems.
Retention: This involves using a tool to determine how long log data should be kept within the log file.
Indexing or Search: A log management tool can help IT personnel filter, sort, analyze, or search data across all logs.
Reporting: Advanced tools are available that can automate reporting from the audit log, which can be useful for operational performance, resource allocation, security, or regulatory compliance purposes.
What is a Log?
Logs are a record of events that occur on a system, such as errors, warnings, and user activity. They are critical to troubleshooting and understanding system behavior.
Not only do applications and operating systems generate logs but devices such as firewalls and routers too.
Moreover, Logs provide vital information about system performance, resource usage, user behavior, and other metrics to help organizations identify potential issues before they become problems.
Logs are time-stamped, enabling IT experts and developers to comprehend the events and when they happened. Additionally, log data is often used for security investigations and compliance purposes.
What are the best Log Management Tools?

Effective log management requires specialized tools and technologies and can be an essential component of an organization’s security and compliance strategy.
There are three categories of Log management tools – open-source, commercial, and cloud-based.
Open-source tools such as Graylog, GoAccess, and Logstash are popular choices among developers. They allow users to easily manage their log data and provide a wide range of features.
Commercial products like Apica, Splunk, Datadog, and Coralogix appeal to larger organizations. These tools offer better scalability, flexibility, and performance than open-source solutions.
Cloud-based log management services such as LogDNA, Amazon CloudWatch, and Loggly are ideal options for businesses that need a simple and cost-effective solution to manage their logs. These services provide easy integration with popular cloud platforms and enable users to monitor and analyze their log data in real-time.
Apica enables you to collect, optimize, analyze, route, and manage log data across your entire stack at any scale, making it easier to build your observability data lake with a single log aggregation tool.
With Apica, you can reduce operational expenses, increase integration with other analytical tools, and improve operational agility.
A good log management solution can help you identify errors quickly, improve system performance, and save money in the long run. Having a strong log management system and plan can provide organizations with valuable real-time information about their system’s health and operations.
No matter what type of solution you decide on, be sure to invest in a reliable logging tool that meets your needs.
Check out the detailed list of the capabilities of the aforementioned Log Management tools here.
The Benefits of Log Management
A successful log management solution can offer several benefits, including:
- Centralized log aggregation, which provides unified data storage.
- Better customer experience by analyzing log data and using predictive modeling.
- Advanced network analytics, which allows for faster and more accurate troubleshooting capabilities.
- Increased security by reducing the attack surface, real-time monitoring, and improved detection and response times.
- Improved observability and visibility across the enterprise with a shared event log.
Apica’s No-Index Log Management at S3 Scale
Database indexes are extremely useful for information systems that require low latency, low throughput, and high consistency. However, creating indexes requires compute and disk space, as well as operational overhead.
In many cases, the resources, time, and cost required to maintain indexing can be greater than the performance benefits of the log management tool itself.
apica.io offers a unique approach to log management with its no-index system, which allows for infinite scaling while maintaining search and query performance. To achieve this, Apica has to address the challenge of infinite scaling for both its data and metadata stores.
Apica stores its metadata in Postgres, but this approach can become costly as it cannot scale infinitely. To address this, Apica has developed a hybrid metadata layer that manages the migration of metadata tables between Postgres and S3. Metadata that is old is seamlessly moved to S3, and is fetched on-demand when needed. The key/value structure of S3 allows for granular metadata retrieval without additional indexes.
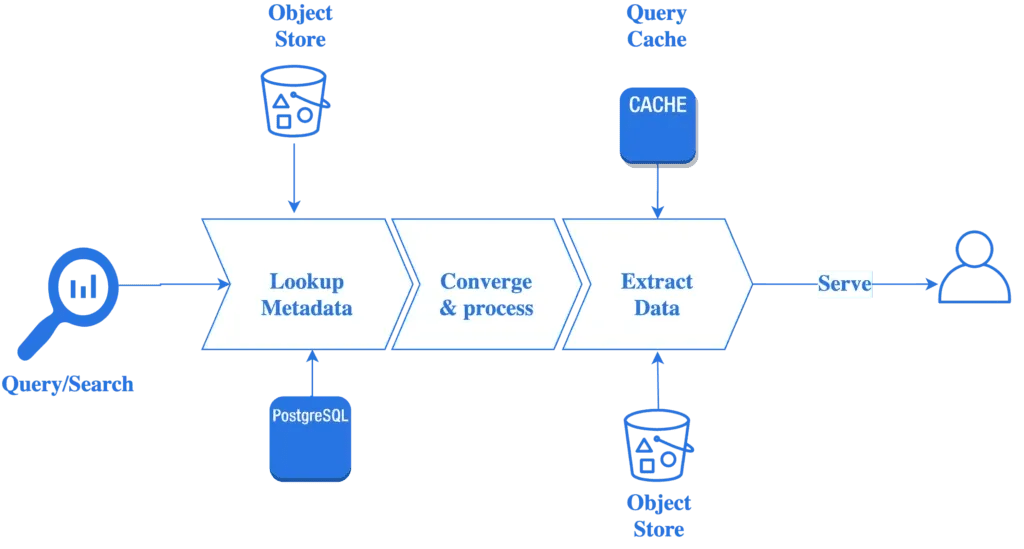
A similar approach is taken with data, where incoming data is stored in partitions and broken down into chunks, so object lookups for a namespace or application do not require additional indexes. The object key encodes the index information, which makes lookups and retrievals efficient when data is needed from the S3 layer that is not stored in the local disk cache.
Apica’s architecture offers several advantages by using S3 as its primary storage location, which includes:
Reduced costs for data and metadata storage
Elimination of costly compute and storage for indexing
Elimination of data egress cost.
Log Management Best Practices
Following are some of the best practices that IT enterprises should consider when investing in a log management system:
Embrace automation tools in order to alleviate the workload
Log management takes time and it can drain resources extensively. With the advent of AI and ML capabilities, the majority of recurring tasks related to data collection and analysis can be automated using advanced tools.
Organizations should consider using automation capabilities and updating old solutions to reduce manual effort when deciding on new log management tools.
Invest in a centralized Log Management system for better accessibility and enhanced security
A centralized log management system not only improves data access but also significantly strengthens the organization’s security capabilities. Storing and connecting data in a centralized location helps organizations quickly detect anomalies and respond to them, reducing the time it takes hackers to laterally penetrate other systems.
Create a monitoring and retention strategy to better manage volume scalability
Leverage cloud technology to improve the ability to scale and be more adaptable.
Invest in a contemporary log management system that operates on cloud technology. Utilizing the cloud allows for greater flexibility and scalability, enabling organizations to adjust their processing and storage capabilities based on fluctuating demands.
Create a personalized policy for monitoring and retaining the data
Log Management with Apica
Apica stands out as a groundbreaking real-time platform that seamlessly integrates the advantages of object store technology, such as scalability, fast retrieval, and data archival, with distributed computing powered by Kubernetes.
In addition to offering flexible dash-boarding, customizable querying, alerting, and search functionalities, Apica also features user-friendly identity management and lifecycle policies. By offering such a comprehensive set of features, Apica significantly reduces operational costs and enhances integration with other analytics tools while improving overall operational agility.
If you want to learn about Apica’s Log management capabilities in more detail, check out our Web Page.
In a Glimpse
- Log management is the process of collecting, monitoring, and analyzing log data to gain insights into an organization’s operations.
- Logs are usually generated by different sources such as operating systems, applications, and network devices and stored in different formats.
- Log management tools include log aggregators, log analysis platforms and security information and event management (SIEM) systems.
- Logs provide crucial information about system performance, resource utilization, user behavior and other important metrics.
- Common log management tools include open-source (i.e., Graylog/Splunk/Logstash), commercial (Apica/Sematext Cloud/Coralogix), cloud-based (LogDNA/Amazon CloudWatch/Loggly) solutions.
- Benefits of proper log management include Centralized log aggregation for unified data storage, better customer experience through predictive modeling; advanced network analytics; increased security; improved observability & visibility; cost reduction & improved integration & agility via Apica’s no-indexing solution.








